Sound - Doppler Effect
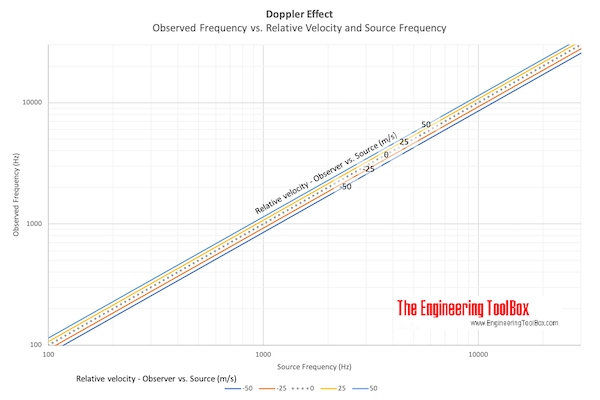
The doppler effect is the change in sound frequency due to the relative motion between a source and a listener.
The change in frequency of sound due to relative motion between a source and a listener is called the Doppler Effect.
The observed sound frequency for a listener can be expressed as
fr = fs (c + vr) / (c + vs) (1)
where
fr = frequency observed by the receiver (1/s, Hz)
fs = frequency emitted from the source (1/s, Hz)
c = speed of sound (m/s)
vr = velocity of the receiver relative to the medium - positive if the receiver is moving towards the source(m/s)
vs = velocity of the source relative to the medium - positive if the source is moving away from the receiver (m/s)
Example - A Train passing a Bell
A train with speed 200 km/h (55.6 m/s) passes a bell with sound frequency 1000 Hz. With an air temperature of 20 oC the speed of sound is 343 m/s.
The frequency observed by a passenger in the train before passing the bell can be calculated as
fr = (1000 Hz) ((343 m/s) + (55.6 m/s)) / ((343 m/s) + (0 m/s))
= 1162 Hz
The frequency observed by the passenger in the train after passing the bell can be calculated as
fr = (1000 Hz) ((343 m/s) + (- 55.6 m/s)) / ((343 m/s) + (0 m/s))
= 838 Hz
Doppler Effect Calculator
Calculate the observed frequency with the calculator below: